Привет, дорогие друзья. Понятие настоящего времени в английском языке не всегда совпадает с нашим. Одним из самых ярких примеров такого различия как раз является Present Perfect.
Present Perfect — настоящее совершенное время — обозначает действие, которое началось в прошлом и завершилось к настоящему моменту. В английском языке глагол в «презент перфект» воспринимается в настоящем времени, а не в прошлом, так как привязан к настоящему результатом.
Правила образования Present Perfect

Простое совершенное время в английском языке образуется с помощью вспомогательного глагола have/has и основного глагола в 3-й форме — в английской грамматике он выполняет роль причастия прошедшего времени.
- I have already eaten my dinner. — Я уже съел свой ужин.
- I cannot go on this trip, my father has fallen ill. — Я не могу поехать в эту поездку, мой отец заболел.
- Has your sister left for Moscow? — Выехала ли ваша сестра в Москву?
Новая статья: Present perfect с упражнениями и ответами
Примеры:

Ben is looking for his key. He can’t find it.
He has Lost his key.
He has Lost his key= He lost it recently, and he still
doesn’t have it.
Have/has Lost is the present perfect simple:
Настоящее совершенное время может употребляться :
— без указания времени совершения действия:
- Have you done your homework? Вы сделали ваше домашнее задание?
— с наречиями неопределенного времени:
ever(когда-либо) / never(никогда) / often(часто) / already(уже) / yet(еще –в отрицательных предложениях, уже- в вопросительных) / just(только что) / lately(недавно)/
- She’s just come back from Italy. Она только что вернулась из Италии.
— с обстоятельственными словами, обозначающими еще не истекшие периоды времени:
today / this week / this month /
- She hasn’t made any phone calls this week. Она не кому не звонила на этой неделе.
Запомните что present perfect tense не употребляется в вопросительных предложениях, начинающихся с наречия when, поскольку в данном случае должно быть указано точное время совершения действия.
Present Perfect
I/we/they/you have (=I’ve, we’ve, etc.) – been, forgotten, written, worked, etc.
He/she/it has (= he’s, she’s etc.) – been, forgotten, written, worked, etc.
When we say that ‘something has happened’, this is usually new information:
Ow! I’ve cut my finger.
The road is closed. There’s been (there has been) an accident.
(from the news) Police have arrested two men in connection with the robbery.
When we use the present perfect, there is a connection with now. The action in the past has a result now:
‘Where’s your key?’ ‘I don’t know. I’ve Lost it.’ (=I don’t have it now)
She told me her name, but I’ve forgotten it. (= I can’t remember it now)
‘Is Tom here?’ ‘No, he’s gone out.’ (=he is out now)
I can’t find my pen. Have you seen it? (= Do you know where it is now?)
Note the difference between gone (to) and been (to):
Ellen is on holiday. She has gone to France. (= She is there now or on her way there)
Tome is back home now. He has been to Italy. (=he has now come back)
You can use the present perfect with just, already and yet.
just = a short time ago:
‘Are you hungry?’ ‘No, I’ve just had lunch.’
Hello. Have you just arrived?
We use already to say that something happened sooner than expected:
‘Don’t forget to pay your electricity bill.’ ‘I ‘ve already paid it.’
‘What time is Sara leaving?’ ‘She’s already Left.’
Yet = until now. Yet shows that the speaker is expecting something to happen. Use yet only in questions and negative sentences:
Has it stopped snowing yet?
She’s written the email, but she haven’t sent it yet.
Диалог
Jane: Have you travelled a lot, Ellen?
Ellen: Yes, I’ve been to lots of places.
Jane: Really? Have you ever been to France?
Ellen: Yes, I’ve been to France once.
Jane: What about Japanese?
Ellen: No, I haven’t been to Japanese.
When we talk about a period of time that continues from the past until now, we use the present perfect (have been I have travelled etc.).
Have you ever eaten apple-pie?
We’ve never had a dog.
Been (to)= visited:
I’ve never been to Egypt. Have you been there?
In the following examples too, the speakers are talking about a period that continues until now
(recently / in the Last few days / so far / since breakfast etc.):
Примеры:
Have you heard anything from Ann recently?
I’ve met a lot of people in the Last few months.
Everything is going well. We haven’t had any problems
so far.
I’m hungry. I haven’t eaten anything since dinner.
(=from dinner until now)
It’s good to see you again. We haven’t seen each other for a Long time.
In the same way we use the present perfect with today I this evening I this year etc. when these periods are not finished at the time of speaking
I’ve drunk five cups of juice today.
Have you had a holiday this month?
I haven’t seen David this afternoon. Have you?
Tom hasn’t worked very hard this term.
We say:
It’s the (first) time something has happened.
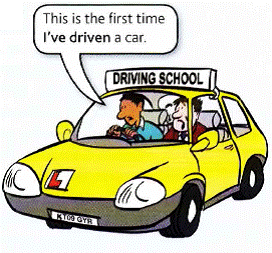
Рассмотрим пример с Елен
Ellen is having a driving lesson. It’s her first one.
It’s the first time She has driven a car. (not drives)
or She has never driven a car before.
Tom has lost his passport again. This is the fourth
time this has happened. (not happens)
Jane is phoning her boyfriend again. That’s the second
time she’s phoned hem this evening.
English Tenses: PRESENT PERFECT
Как видите, Present Perfect не кажется таким уж нелогичным и непонятным, если в нем разобраться. Кроме того, у этого времени очень много слов-спутников – наречий, которые помогают нам распознать настоящее совершенное время.
 Английский с нуля Уроки английского языка для начинающих
Английский с нуля Уроки английского языка для начинающих